A feature that has been around in SharePoint for a while now is the
capability to set site collections and content databases to read only –
the former being a property on the site collection in SharePoint and the
latter by setting the database directly in SQL Server. This feature
hides and disables all the write-based functions on a site, for example,
uploading documents, creating and editing list items, etc.
It is commonly used in migration scenarios to prevent users from adding content whilst their sites are being moved to a new platform – once the migration has been completed then their site collections can be set back to read/write again.
The easiest, and perhaps most fool-proof way to do this is to set the database as read only in SQL Server, as this will disable the write function on all site collections in one quick change. However, there may be occasions where you may prefer to set it at the site collection level. Typically, this is preferred in scenarios where you wish to enable or disable the read only feature on individual site collections at different times during a migration, perhaps where there is more urgency to control read/write access for specific teams either earlier or later in the migration phase.
The script in this article walks through each Web application (except Central Administration), each content database mounted to the Web application, and finally each site collection in the content database and sets the ReadOnly property to either True (content cannot be created) or False (content can be created). I have also built in an “excluded paths” feature, that allows you to specify individual site collections or entire Web applications from being modified by the script.
First, launch the SharePoint Management Shell (or preferred alternative PowerShell editor) and type the following line to choose whether to set the ReadOnly property to True or False. In the example, I am going to set site collections to read only mode:
Note: Each URL is in quotes and comma-separated:

It is commonly used in migration scenarios to prevent users from adding content whilst their sites are being moved to a new platform – once the migration has been completed then their site collections can be set back to read/write again.
The easiest, and perhaps most fool-proof way to do this is to set the database as read only in SQL Server, as this will disable the write function on all site collections in one quick change. However, there may be occasions where you may prefer to set it at the site collection level. Typically, this is preferred in scenarios where you wish to enable or disable the read only feature on individual site collections at different times during a migration, perhaps where there is more urgency to control read/write access for specific teams either earlier or later in the migration phase.
The script in this article walks through each Web application (except Central Administration), each content database mounted to the Web application, and finally each site collection in the content database and sets the ReadOnly property to either True (content cannot be created) or False (content can be created). I have also built in an “excluded paths” feature, that allows you to specify individual site collections or entire Web applications from being modified by the script.
First, launch the SharePoint Management Shell (or preferred alternative PowerShell editor) and type the following line to choose whether to set the ReadOnly property to True or False. In the example, I am going to set site collections to read only mode:
# Define whether ReadOnly will be set to true or falseNext, build the $excludedPaths variable to specify any site collections or Web applications that you wish to exclude from modification by the script. If you would like the script to exclude entire Web applications, then you must add a trailing slash to the URL – e.g., “http://mysite.domain.lab/”. To exclude site collections only, leave off the trailing slash – e.g., “http://mysite.domain.lab”. This functionality allows you to exclude root site collections from being modified but not the entire Web application – for example, you may want to leave the My Site Host site collection read/write but set all the personal sites in the My Site Web application to read only.
[bool]$readOnly = $true
Note: Each URL is in quotes and comma-separated:
# Set excluded paths as comma-delimited stringsNow the remainder of the script, which will walk through each site collection in the farm, setting the ReadOnly property as explained earlier:
# Note: Web applications must end in a trailing slash, where site collections do not
[array]$excludedPaths = "http://applications.domain.lab/",
"http://mysite.domain.lab",
"http://portal.domain.lab/sites/siteA",
“http://portal.domain.lab/search”
# Get all Web applications (except Central Admin)The script above will display a list of modified site collections in the PowerShell console as it changes them, and also confirm the Web applications and site collections that were excluded from the process. Should you lose track of which site collections have been set to read only and which ones haven’t, then you can easily generate a status report in the console by using the following script:
Get-SPWebApplication | ForEach-Object {
if ($excludedPaths -notcontains $_.Url)
{
# Enumerate all content databases in each Web application
if ($_.ContentDatabases -ne $null) {
$_.ContentDatabases | ForEach-Object {
# Enumerate all site collections in each content database
if ($_.Sites -ne $null) {
$_.Sites | ForEach-Object {
# Check if there are sites where the property should not be changed
if ($excludedPaths -notcontains $_.Url)
{
Write-Host "Changing ReadOnly property for site" $_.Url
# Set ReadOnly property
$_.ReadOnly = $readOnly
Write-Host "ReadOnly property for site" $_.Url "set to" $_.ReadOnly
# Dispose site collection object
$_.Dispose()
}
else
{
# Confirm if no changes made on excluded sites
Write-Host "No changes made for site" $_.Url
}
}
}
}
}
}
else
{
# Confirm if no changes made on excluded web applications
Write-Host "No changes made for web application" $_.Url
}
}
# Get all Web applications (except Central Admin)For additional info, the scripts in this article could be used to get or set other site collection properties, too. For example, the Portal Site Connection property, SharePoint Designer permissions, or Site Collection Administrators. See this article on MSDN for a full list of properties available for configuration on site collections, including ReadOnly.
Get-SPWebApplication | ForEach-Object {
# Enumerate all content databases in each Web application
if ($_.ContentDatabases -ne $null) {
$_.ContentDatabases | ForEach-Object {
# Enumerate all site collections in each content database
if ($_.Sites -ne $null) {
$_.Sites | ForEach-Object {
Write-Host "ReadOnly property for site" $_.Url "set to" $_.ReadOnly
# Dispose site collection object
$_.Dispose()
}
}
}
}
}
Force stop and then start a full crawl on all content sources in a SharePoint 2010 farm using PowerShell
There have been many times where I have needed to run a full crawl of
all content sources on a SharePoint 2010 farm, but I quite often there
are already crawls taking place, which I prefer to stop before starting a
new one.
The script below walks through each content source and does the following:

The script below walks through each content source and does the following:
- Checks whether the crawl status is set to “Idle”
- If the content source is currently involved in a crawl activity, stop the activity and wait until the status changes back to Idle
- If the content source is Idle, then start a full crawl
Get-SPEnterpriseSearchCrawlContentSource -SearchApplication "Search Service Application" | ForEach-Object {For info, you can use the following script if you want to display the crawl status of all content sources on your farm:
if ($_.CrawlStatus -ne "Idle")
{
Write-Host "Stopping currently running crawl for content source $($_.Name)..."
$_.StopCrawl()
do { Start-Sleep -Seconds 1 }
while ($_.CrawlStatus -ne "Idle")
}
Write-Host "Starting full crawl for content source $($_.Name)..."
$_.StartFullCrawl()
}
Get-SPEnterpriseSearchCrawlContentSource -SearchApplication "Search Service Application" | select Name, CrawlStatusThis will give you an output similar to the following:

Start all enabled timer jobs on a SharePoint 2010 farm using PowerShell and check their status
Starting a timer job is fairly easy with PowerShell on SharePoint
2010 using the Start-SPTimerJob command, but the script below walks
through each timer job in the farm, checks that it is enabled for use
(there’s not much point in trying to start a disabled timer job!), and
then starts it:
If you want to look at a report of the current status of each timer job, run the following script:

Get-SPTimerJob | where { $_.IsDisabled -eq $false } | sort $_.Name | ForEach-Object {This can be quite useful if you want to run everything in the farm before performing maintenance or as a test to ensure all timer jobs are operating successfully. Note that the script will report whether it is starting the timer job at the farm level or for each web application.
try
{
$timerJobName = $_.Name
if ($_.WebApplication -ne $null) { $waMessage = "on web application $($_.WebApplication.Url)" }
else { $waMessage = "on Farm" }
Start-SPTimerJob -Identity $_
Write-Host "Started timer job $timerJobName $waMessage"
}
catch
{
Write-Host "There was a problem starting timer job $timerjobName:" $_
}
}
If you want to look at a report of the current status of each timer job, run the following script:
function Get-SPTimerJobStatusThis will produce a grid view showing each timer job, whether it was run at the farm or web application level, and the last run status, as shown in the example screenshot below:
{
Get-SPTimerJob | sort Name | ForEach-Object {
$lastRun = $_.HistoryEntries | Select-Object -first 1
if ($_.WebApplication -eq $null) { $level = "Farm" }
else { $level = $_.WebApplication.Url }
$values = @{
"Name" = $_.Name
"Level" = $level
"StartTime" = $lastRun.StartTime
"EndTime" = $lastRun.EndTime
"Status" = $lastRun.Status
}
New-Object PSObject -Property $values | Select @("Name","Level","StartTime","EndTime","Status")
}
}
Get-SPTimerJobStatus | Out-GridView

Sending SharePoint system notification e-mails using PowerShell
The script in this article demonstrates an example of how you could
use PowerShell to send system notification e-mails to administrators on a
scheduled basis. Of course, there are a number of ways to do this sort
of thing, including SharePoint workflows, Microsoft SCOM, and custom
code. I’m not saying PowerShell is necessarily better than these
methods, but I like the flexibility it brings, and as you have full
access to the Object Model, you could send notifications from all sorts
of areas – for example, successes and errors from the crawl logs,
information from the User Profile service application, timer jobs with
last run times, list items, site users, etc.
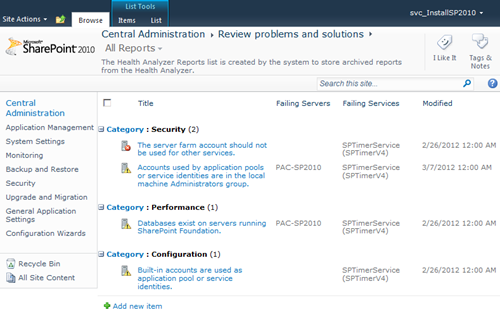
The example I have chosen here is to send an HTML e-mail listing the currently active items from the SharePoint Health Analyzer. This information is effectively just stored in a SharePoint list on the Central Administration site, so I will need to access the list, query the active items and send this information using the SMTP mail server and reply addresses specified in the farm outbound e-mail settings.
First of all we need to get the Central Administration web application and site objects from the farm. Note that we do not need to specify any URLs here - The command will automatically find Central Administration using options provided in the SharePoint 2010 cmdlets:

The example I have chosen here is to send an HTML e-mail listing the currently active items from the SharePoint Health Analyzer. This information is effectively just stored in a SharePoint list on the Central Administration site, so I will need to access the list, query the active items and send this information using the SMTP mail server and reply addresses specified in the farm outbound e-mail settings.

First of all we need to get the Central Administration web application and site objects from the farm. Note that we do not need to specify any URLs here - The command will automatically find Central Administration using options provided in the SharePoint 2010 cmdlets:
#Get Central Admin Web Application and Web objectsNext we can specify the user or group e-mail address that will receive the message, followed by the sender’s e-mail address and the name of the SMTP server sending the message, which I am taking from the farm outbound e-mail settings stored in the Central Administration web application. If you want to send the message to more than one user or group, you could set up an array and walk through each item.
$caWebApp = (Get-SPWebApplication -IncludeCentralAdministration) | ? { $_.IsAdministrationWebApplication -eq $true }
$caWeb = Get-SPWeb -Identity $caWebApp.Url
#Set up from, to and server addressesThe following part of the script gets the Health Analyzer list (internal name “HealthReports”) and the default display form URL. We need this URL later when configuring hyperlinks in the HTML, so that users can click on a health report directly from the e-mail to show it in the browser.
$toAddress = "svc_installsp2010@domain2010.lab"
$fromAddress = $caWebApp.OutboundMailReplyToAddress
$serverAddress = $caWebApp.OutboundMailServiceInstance.Server.Address
#Get Health Analyzer list on Central Admin siteThis is probably the trickiest part of the script as it uses a CAML query to find all items in the Health Analyzer, except for those with the Severity column set to “4 – Success”. In other words, it queries any item that the Health Analyzer considers to be a problem on the farm. The CAML itself is specified in the first line below – I’m not going to go into how to write this stuff as there are quite a number of references available on the Internet already.
$healthList = $caWeb.GetList("\Lists\HealthReports")
$displayFormUrl = $caWeb.Url + ($healthList.Forms | where { $_.Type -eq "PAGE_DISPLAYFORM" }).ServerRelativeUrl
$queryString = "<Where><Neq><FieldRef Name='HealthReportSeverity' /><Value Type='Text'>4 - Success</Value></Neq></Where>"This next section creates the subject and HTML body for the e-mail message. If you know HTML then you will see what is happening, and if you don’t then that’s another subject for you to learn! The key part from a SharePoint perspective is the foreach ($item in $items) routine, as this is where the script walks through each list item found from the query above and injects the column values into the HTML. Note where the $displayFormUrl variable is used from earlier to set up the URL used for the hyperlink. I’m also using the built-in ConvertTo-Html PowerShell cmdlet to format the HTML.
$query = New-Object Microsoft.SharePoint.SPQuery
$query.Query = $queryString
$items = $healthList.GetItems($query)
#Set up e-mail message subject and HTML bodyFinally, the commands below use the System.Net.Mail .NET class to send the e-mail, using the IsBodyHtml boolean property to ensure it goes as an HTML message.
$msgTitle = "Health Analyzer results for farm " + $caWebApp.Farm.Name + " - " + (Get-Date)
#HTML head
$head = "<style type=`"text/css`">.tableStyle { border: 1px solid #000000; }</style>"
$head = $head + "<Title>$msgTitle</Title>"
#Create HTML body by walking through each item and adding it to a table
$body = "<H2>$msgTitle</H2><table cellspacing=`"0`" class=`"tableStyle`" style=`"width: 100%`">"
foreach ($item in $items)
{
$itemUrl = $displayFormUrl + "?id=" + $item.ID
[array]$itemValues = @($item["Severity"], $item["Category"], $item["Explanation"], $item["Modified"])
$body = $body + "<tr>"
$body = $body + "<td class=`"tableStyle`"><a href=`"" + $itemUrl + "`">" + $item.Title + "</a></td>"
$itemValues | ForEach-Object {
$body = $body + "<td class=`"tableStyle`">$_</td>"
}
$body = $body + "</tr>"
}
$body = $body + "</table>"
#Create message body using the ConvertTo-Html PowerShell cmdlet
$msgBody = ConvertTo-Html -Head $head -Body $body
#Create e-mail message object using System.Net.Mail classThat’s it! The e-mail will be sent when the script is run and should look similar to the one shown below. As you can see, the items in the e-mail match up to the items shown in the Health Analyzer screenshot at the beginning of this article.
$msg = New-Object System.Net.Mail.MailMessage($fromAddress, $toAddress, $msgTitle, $msgBody)
$msg.IsBodyHtml = $true
#Send message
$smtpClient = New-Object System.Net.Mail.SmtpClient($serverAddress)
$smtpClient.Send($msg)
$caWeb.Dispose()

Managing, creating and deleting SharePoint list views with PowerShell
Due to the number of configuration options available, manipulating
list views through PowerShell can be quite involved and I certainly
wouldn’t recommend it if you only have a few lists to change. However,
when there are a large number of views and lists involved, PowerShell
can significantly reduce the amount of time needed to manage and
configure them.
For this example, I have created a new view called “Sort by modified date”, which is effectively the same as the default “All Documents” view but with the items ordered by modified date in descending order. I have also added the “File Size” column to the view and specified a limit of 50 items per page.
Once this is done, type the following set of commands to display the properties of the new view:
When creating the view in PowerShell, you will need to use some of these properties as mandatory parameters in the script. These mandatory properties are listed below:
Manage List Views
The first stage is looking at the commands to manage available views on a list. For this example, I am going to get the “Shared Documents” document library from a root site and assign it to a variable called $list:$web = Get-SPWeb http://portalTo find the title and URL of the current default view, type the following command:
$list = $web.GetList(($web.ServerRelativeUrl.TrimEnd("/") + "/Shared Documents"))
$list.DefaultView | select Title, UrlIf you want to show one of the non-default views then you can call it with the display name, as follows:
$list.Views["Test View"]To change the default view for the list, type the following set of commands for the view you want to configure as the new default:
$view = $list.Views["Test View"]
$view.DefaultView = $true
$view.Update()
Create New List Views
The easiest way to create a list view using PowerShell is to create one in the UI first with all the settings you need. You can then use the properties of the view you have created to define the parameters required for the view creation script we use later in this section.For this example, I have created a new view called “Sort by modified date”, which is effectively the same as the default “All Documents” view but with the items ordered by modified date in descending order. I have also added the “File Size” column to the view and specified a limit of 50 items per page.
Once this is done, type the following set of commands to display the properties of the new view:
$web = Get-SPWeb http://portalYou should now see a long list of property names and associated values for this view, including Title, Query, RowLimit and ViewFields (i.e., columns). You can also take a look at the value of any one of these properties individually by typing $newview.PropertyName and hitting Enter. For example, to get a full list of ViewFields, type $newview.ViewFields.
$list = $web.GetList(($web.ServerRelativeUrl.TrimEnd("/") + "/Shared Documents"))
$newview = $list.Views["Sort by modified date"]
$newview
When creating the view in PowerShell, you will need to use some of these properties as mandatory parameters in the script. These mandatory properties are listed below:
#Get destination site and listYou may have a requirement to add this list view to the “Shared Documents” library on every site in a site collection. To do this, we need to wrap the Add method in a ForEach-Object condition for every site in a specified site collection. This script will also report an issue if the Shared Documents library does not exist on one or more sites:
$web = Get-SPWeb "http://portal/sites/testsite"
$list = $web.GetList(($web.ServerRelativeUrl.TrimEnd("/") + "/Shared Documents"))
$viewTitle = "Sort by modified date" #Title property
#Add the column names from the ViewField property to a string collection
$viewFields = New-Object System.Collections.Specialized.StringCollection
$viewFields.Add("DocIcon") > $null
$viewFields.Add("LinkFilename") > $null
$viewFields.Add("Modified") > $null
$viewFields.Add("Editor") > $null
$viewFields.Add("FileSizeDisplay") > $null
#Query property
$viewQuery = "<OrderBy><FieldRef Name='Modified' Ascending='FALSE'/></OrderBy>"
#RowLimit property
$viewRowLimit = 50
#Paged property
$viewPaged = $true
#DefaultView property
$viewDefaultView = $false
#Create the view in the destination list
$newview = $list.Views.Add($viewTitle, $viewFields, $viewQuery, $viewRowLimit, $viewPaged, $viewDefaultView)
Write-Host ("View '" + $newview.Title + "' created in list '" + $list.Title + "' on site " + $web.Url)
$web.Dispose()
#Title propertyBy the way, if you create a new view with the same title as one that already exists on a list, it will create an extra view in that list with the same title – not overwrite the previous one.
$viewTitle = "Sort by modified date"
#Add the column names from the ViewField property to a string collection
$viewFields = New-Object System.Collections.Specialized.StringCollection
$viewFields.Add("DocIcon") > $null
$viewFields.Add("LinkFilename") > $null
$viewFields.Add("Modified") > $null
$viewFields.Add("Editor") > $null
$viewFields.Add("FileSizeDisplay") > $null
#Query property
$viewQuery = "<OrderBy><FieldRef Name='Modified' Ascending='FALSE'/></OrderBy>"
#RowLimit property
$viewRowLimit = 50
#Paged property
$viewPaged = $true
#DefaultView property
$viewDefaultView = $false
#Get the site collection
Get-SPSite "http://portal/sites/testsite" | Get-SPWeb -Limit All | ForEach-Object {
$webUrl = $_.Url
try
{
#Get the Shared Documents library
$list = $_.GetList(($_.ServerRelativeUrl.TrimEnd("/") + "/Shared Documents"))
#Create the view in the destination list
$newview = $list.Views.Add($viewTitle, $viewFields, $viewQuery, $viewRowLimit, $viewPaged, $viewDefaultView)
Write-Host ("View '" + $newview.Title + "' created in list '" + $list.Title + "' on site " + $webUrl)
}
catch
{
Write-Host ("There was a problem trying to create the view in the site " + $webUrl + ": " + $_)
}
}
Modify Existing List Views
The scripts above create list views with a limited set of mandatory properties, but there are probably some extra properties that you will also want to set on views. As mentioned earlier, to help you decide which settings you need to configure on a view using PowerShell, create a view in the UI first and list its properties and values by running this script:$web = Get-SPWeb http://portalFor a full description of the properties and methods available for configuring views, please see this article on MSDN. Once you have decided which properties you wish to set, look up the values of the view you created in the UI and use this script to modify a view’s settings using PowerShell. In this example, we will be changing the “Sort by modified date” view configured on the Shared Documents library in site http://portal/sites/testsite so that it can be accessed as a mobile view and is set as the default mobile view for the list:
$list = $web.GetList(($web.ServerRelativeUrl.TrimEnd("/") + "/Shared Documents"))
$newview = $list.Views["Sort by modified date"]
$newview
#Get the site and list
$web = Get-SPWeb "http://portal/sites/testsite"
$list = $web.GetList(($web.ServerRelativeUrl.TrimEnd("/") + "/Shared Documents"))
#Get the list view to be changed
$newview = $list.Views["Sort by modified date"]
#Set the mobile and default mobile view properties
$newview.MobileView = $true
$newview.MobileDefaultView = $true
#Update the view configuration
$newview.Update()
$web.Dispose()
Delete List Views
Finally, here is a script to delete a list view. The obvious thing to mention here is being careful not to delete the default view on a list, or if you want to, ensure that you change the default view to another one first before doing so. The name of the view we are going to delete in this example is “Sort by modified date” in the Shared Documents library on site http://portal/sites/testsite:#Get the site and list
$web = Get-SPWeb "http://portal/sites/testsite"
$list = $web.GetList(($web.ServerRelativeUrl.TrimEnd("/") + "/Shared Documents"))
#Get the list view to be changed
$newview = $list.Views["Sort by modified date"]
#Delete this view from the list
$list.Views.Delete($newview.ID)
$web.Dispose()
Resetting the SharePoint 2010 search index using PowerShell
The script here resets the SharePoint 2010 search index, which I have
posted as there is no out-of-the-box cmdlet for doing this. This
effectively does the same thing as the Index Reset option for the search service application in Central Administration:

Note there are two parameters you can specify in the Reset method:

Note there are two parameters you can specify in the Reset method:
- Disable alerts: $true if the Search alerts should be disabled during reset; otherwise, $false. Selecting $true here is the same as ticking the “Deactivate search alerts during reset” checkbox shown in the screenshot above.
- Ignore unreachable server: $true if the failures to connect to servers are ignored; otherwise, $false.
#Get the search service application
#You will need to specify the -Identity switch and a name if you have more than one
$sa = Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplication
#Reset index with the following options in brackets:
#Disable Alerts $true/$false
#Ignore unreachable server $true/$false
try
{
Write-Host "Attempting to reset the index...please wait"
$sa.Reset($false, $false)
Write-Host "Index successfully reset" -ForegroundColor Blue
}
catch
{
Write-Host "There was a problem resetting the index:" $_ -ForegroundColor Red
}
Perform an IISRESET on multiple servers using PowerShell
#Specify servers in an array variableTo use the script, simply replace the server names with those from your SharePoint farm and run on one of the servers.
[array]$servers = "Server1","Server2","Server3","Server4"
#Step through each server in the array and perform an IISRESET
#Also show IIS service status after the reset has completed
foreach ($server in $servers)
{
Write-Host "Restarting IIS on server $server..."
IISRESET $server /noforce
Write-Host "IIS status for server $server"
IISRESET $server /status
}
Write-Host IIS has been restarted on all servers
The script will also output the status of all IIS related services from each server using the IISRESET /status switch.



Comments